Truth definition the true or actual state of a matter. A foundational principle of philosophy is being able to discern between truth and error or as Thomas Aquinas observed It is the task of the philosopher to make distinctions Challenges to Truth.
 What Is Truth What Does Truth Mean Truth Meaning Definition How To Pronounce Truth Youtube
What Is Truth What Does Truth Mean Truth Meaning Definition How To Pronounce Truth Youtube
Truth in philosophy the property of sentences assertions beliefs thoughts or propositions that are said in ordinary discourse to agree with the facts or to state what is the case.

What is truth definition. Heres a simple definition drawn from what the Bible teaches. Because the definition of truth flows from God truth is theological. Notice that the Old English meaning of true was steadfast loyal and truth meant faithfulness constancy 6 The concept of loyalty and faithfulness is still preserved in expressions such as a true friend or being true to something eg oneself.
A statement about the way the world actually is. There are different theories on truth such as. Synonyms What is truth.
Truth is usually held to be the opposite of falsehoodThe concept of truth is discussed and debated in various contexts including philosophy art. Philosophers and scientists have debated the issue of absolute truth for centuries. In short truth is simply telling it like it is.
Bible Dictionaries - Bakers Evangelical Dictionary of Biblical Theology - Truth Truth N T E In Scripture truth is characterized by both qualitative and quantitative aspects. A verified or indisputable fact. In truth he was not qualified for the job.
It is also one of the largest. The referendum was the first major vote in the era of post-truth politics. The body of real things events and facts.
Translation English dictionary definition of What is truth. He dubs the current administration a post-truth White House. Pronunciation What is truth.
That which is true cannot be self-contradictory. In the historical narratives of the Old Testament truth is identified with personal veracity and historical factuality. He tried to find out the truth.
Conformity with fact or reality. ˌpoʊstˈtruːth relating to a situation in which people are more likely to accept an argument based on their emotions and beliefs rather than one based on facts. Truth is the self-expression of God.
Truth is the property of being in accord with fact or reality. Major theories of truth include those based on correspondence coherence truth conditions and deflationism. The real facts about a situation event or person.
Truth is a property not so much of thoughts and ideas but more properly of beliefs and assertions. Coherence theory of truth says that truth is a set of coherent propositions from which truth statements are developed. The quality of being true.
Truth definition is - the body of real things events and facts. Define What is truth. Or ones word promise or convictions.
Truth is that which is consistent with the mind will character glory and being of God. How to use truth in a sentence. Does this story have any truth.
The word truth is defined as the true or actual state of a matter. But to believe or assert something is not enough to make it true or else the claim that to. Conformity to fact or actuality.
So what is truth. Truth has been a topic of discussion in its own right for thousands of years. The actual state of things.
Moreover a huge variety of issues in philosophy relate to truth either by relying on theses about truth or implying theses about truth. Simply we can define truth as. It is the way things really are and any other viewpoint is wrong.
Even more to the point. The nature of truth is debated but truth is a statement that accurately reflects reality logic andor morality. Truth is one of the central subjects in philosophy.
Moreover many others have chosen to accept another philosophy called situation ethics. A transcendent fundamental or spiritual reality. That is the biblical meaning of truth.
The state of being the case. In contracts the parties are bound to toll the truth in their dealings and a deviation from it will generally avoid the contract. In everyday language truth is typically ascribed to things that aim to represent reality or otherwise correspond to it such as beliefs propositions and declarative sentences.
Well look at various theories below that philosophers have considered but thats an adequate rough-and-ready definition to get us started.
See Victoria et al. Hunger is a problem that most often affects low-income families because living in poverty means that people are often going without basic needs such as food clothing and adequate shelter.
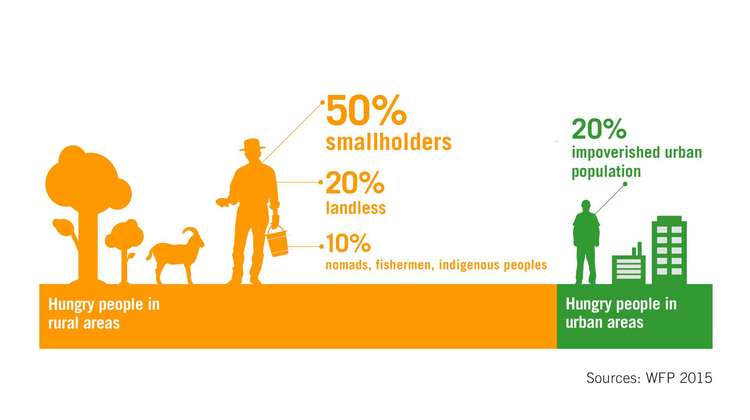 Hunger Facts Figures Welthungerhilfe
Hunger Facts Figures Welthungerhilfe
In addition to causing hunger poverty limits a rural communitys ability to invest in its own development.
Hunger and poverty definition. The target of reducing extreme poverty rates by half was met five years ahead of the 2015 deadline. Physical and psychological effects of deprivation of quality food are likely to deepen poverty. This contributes to the disparity in the eduction of rural and urban girls.
Poverty and hunger are often caused by lack of education employment and. Halve the proportion of people who suffer from hunger. It is Time to Think Globally and Act Locally Developed countries are not immune to hunger and malnutrition.
Poverty is being sick and not being able to see a doctor. UNICEF European Union 2014 The ultimate manifestation of poor nutrition is malnutrition due to basic underlying and immediate factors that contribute to this condition. Poverty is being sick and not being able to see a doctor.
Poverty is lack of shelter. Both food insecurity and obesity are the consequences of poverty and a lack of access to nutritious food. In 1990 nearly half of the.
Here are some widely accepted definitions of key terms. Rural households are the most heavily burdened by the consequences of poverty and hunger. Poverty is not having access to school and not knowing how to read.
Someone who is poor has insufficient money for food but also cannot provide for their own health and cannot invest in education for children. The threshold for food deprivation or undernourishment is fewer than 1800 calories per day. Hunger is above all a consequence of poverty.
This does not mean that the two are necessarily causally linked. Poverty is losing a child to illness brought about by unclean water. Globally there is evidence of improvements in childrens nutritional status.
And since 2000 44 million more people in this country are living in poverty. Some of the most abject poverty in the world is concentrated in farming communities. In order for a child to have a chance at a bright future they need to eat healthy meals every day.
Poverty is powerlessness lack of representation and freedom. Only site-appropriate agriculture can combat poverty and hunger. In other words not knowing where the next meal is coming from.
Poverty is the number one cause of hunger since it results in a lack of ability to buy food and pay for the expansion of agricultural programs. Food insecurity is the more formal term for this condition. Somewhat paradoxically it often correlates with obesity as well.
Hunger can be viewed as a dimension of extreme poverty. Poverty is not having access to school and not knowing how to read. The FAO definitions differentiate hunger from malnutrition and food insecurity.
Malnutrition results from deficiencies excesses or imbalances in the consumption of macro- andor micro-nutrients In the FAO definition all hungry people suffer from malnutrition but people who are malnourished may not be hungry. Millions of Americans live in poverty more families are suffering and hunger is seen growing. Poverty and hunger are closely linked - those who live in poverty are likely to suffer from hunger or malnutrition.
Often rural girls living in poverty will be kept out of school to save money. By causing poor health small body size low levels of energy and reductions in mental functioning hunger can lead to even greater poverty by reducing peoples ability to work and learn thus leading to even greater hunger. Hunger is a result of the immediate causes of malnutrition.
Hunger is also a cause of poverty and thus of hunger in a cyclical relationship. Undernutrition goes beyond calories to signify deficiencies in energy protein andor essential vitamins and minerals. Poverty is not having a job is fear for the future living one day at a time.
A month of bad weather for a farmer or an illness for a worker and a loss of income can mean less food and the prospect of hunger. Women are usually particularly disadvantaged. People in certain conditions whether they live in the developing world or the United States are extremely vulnerable to hunger.
According to the most recent Census Bureau statistics nearly 36 million Americans lived in poverty in 2003 an increase of 13 million from 2002. Many farm women children and men depend on a precarious balance of multiple livelihoods in which hunger is a daily fact of life and where access to basic services education health and water supplies is even more difficult than for the urban poor. The technical term for this phenomenon is food insecurity.
Today food insecurity is not only associated with hunger. Eradicate extreme poverty and hunger. It is often called the most severe and critical manifestation of poverty.
Poverty is lack of shelter. Hunger is the distress associated with lack of food. Its manifestations include hunger and malnutrition limited access to education and other.
Another definition of hunger involves the mental uncertainty of future access to food. Poverty entails more than the lack of income and productive resources to ensure sustainable livelihoods. Living in poverty may lead to hunger and malnutrition which affect childrens and adults ability to concentrate at school or work.
The positive aspects of some countries serve to attract more immigrants than others. In geographical terms the push-pull factors are those that drive people away from a place and draw people to a new location.
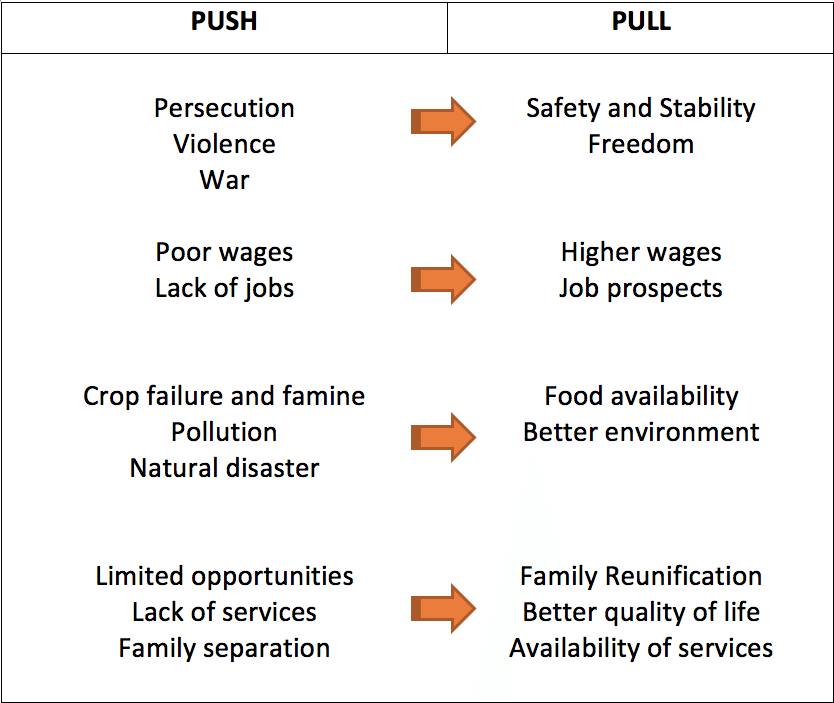 Root Causes Of Migration Justice For Immigrants
Root Causes Of Migration Justice For Immigrants
Something that attracts people to a place or an activity.
Push and pull factors definition. Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools. As against this pull strategy encourages the customer to seek the product or brand. These include a chance of a better job better education a better standard of.
In pull strategy communication of products or information is demanded by the buyer while in push strategy no such communication is demanded. Pull factors are those which encourage a person to move. Push and Pull Factors.
Therefore a pull is the force of bringing an object closer. Something that attracts people to. What Factors Make Latin America The Worlds Most Violent Region.
These factors are what pushes people away from a location and what draws them to move to a new location. Pull factors are those factors in the destination country that attract the individual or group to leave their home. Those factors are known as place utility which is the desirability of a place that attracts people.
Push And Pull Factors Of Migration Juan Ramos on November 24 2017 Leave a Comment. Something that attracts people to. A migrant is more likely to perceive push factors more accurately than pull factors because he is more familiar with the place where he is living than the place that he is moving too.
A push and a pull are opposite forces meaning they move objects in different directions. We use the force of a pull when we move our. Pull Factors are positive aspects that attract people to move to a place eg good employment opportunites.
These factors deal in combination with each other during the process of migration. Push Factors are negative things that make people want to move to a new area eg war. People that cant find a job are often drawn to a pull factor of a country where it is easier to find jobs in their field of expertise.
Push factors are those that encourage a migrant to leave his place of residence. Other push factors include race and discriminating cultures political intolerance and persecution of people who question the status quo. Better economic opportunities more jobs and the promise of a better life often pull people into new locations.
The push and pull factors are the faces of a same coin showing how living conditions human rights society and many other parts of the mosaic can influence common lives. Below are three examples of pull factors that draw migrants to receiving countries. Something that attracts people to a place or an activity.
Producer promotes product wholesalers wholesalers promote product to retailers retailers promote product to consumers. Push strategy aims at making customer aware of the product or brand. While in Push strategy.
Push and pull factors of migration are driven by the push of conflict extreme hardship war lack of economic opportunities etc. A combination of push-pull factors helps determine migration or immigration of particular populations from one land to another. By examining these factors we can further explore migrations and they help us understand them better.
A push promotional strategy makes use of a companys sales force and trade promotion activities to create consumer demandfor a product. The push and pull factors are terms used when talking about the topic of migration. Push-and-pull factors Quick Reference In the study of migration push factors are those that encourage a population to leave its home pull factors are those that draw a population to another area or place.
Knowing these factors. Push-and-pull factors published on by Oxford University Press. Start studying Push and Pull Factors.
Safeopedia explains Pull Factors People often migrate to places with better pull factor to escape places with push factors such as natural disasters persecution poor opportunities etc. Used in geography and globalization pull factor is a positive term used to explain what makes a place attractive to those migrating from a different land. For example a young adult who cannot find a lucrative job in their home country may consider immigrating only if the opportunities are significantly better elsewhere.
Push factors are those which force a person to move. Combined with the pull of more jobs the promise of a better life freedom to practice ones religion etc. Whereas push factors drive migrants out of their countries of origin pull factors are responsible for dictating where these travelers end up.
It takes the product to the customer - the customer knows about the product when they buy it. Migration can occur as result of push and pull factors. This can include drought famine lack of jobs over population and civil war.
Those that have these features belong to other types. It can grow into the rest.
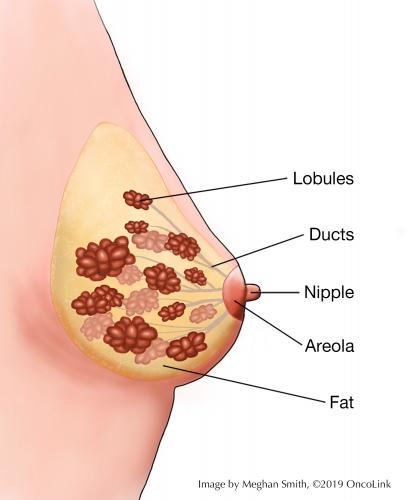 Understanding Your Pathology Report Breast Cancer Oncolink
Understanding Your Pathology Report Breast Cancer Oncolink
4 It simply means that abnormal cells have passed through a thin layer of tissue called the basement membrane and have the potential to spread.

Invasive breast cancer definition. When breast cancer is invasive it starts in the breast ducts or glands but grows into. Breast cancer is a type of cancer that starts in the breast. 4 An Overview Invasive Ductal Carcinoma IDC.
In-VAY-siv brest KAN-ser Cancer that has spread from where it began in the breast to surrounding normal tissue. The most common type of breast cancer invasive ductal carcinoma begins in the milk duct but has grown into the surrounding normal tissue inside the breast. Cancer cells spread from the lobules to the breast tissues that are close by.
Have a 1 in 8 chance of developing an invasive form of breast cancer during their lifetime. The most common type of invasive breast cancer is invasive ductal carcinoma which begins in the lining of the milk ducts thin tubes that carry milk from the lobules of the breast to the nipple. Ipsilateral invasive breast tumor recurrence IIBTR.
Invasive breast cancer in the axilla regional lymph nodes chest wall and skin of the ipsilateral breast. The most common kinds of breast cancer are Invasive ductal carcinoma. The cancer cells grow outside the ducts into other parts of the breast tissue.
Most invasive breast cancers have no special features and are classed as No Special Type. D uctal C arcinoma I n- S itu DCIS refers to breast cells that are growing abnormally in an area of the breast but have not yet evolved to the point where they are considered invasive breast cancer and can spread beyond the breast to other parts of the body. Most breast cancers are invasive but there are different types of invasive breast cancer.
DCIS is noninvasive meaning it hasnt spread out of the milk duct and has a low risk of becoming invasive. Invasive ductal carcinoma begins in the milk ducts of the breast and invades the surrounding breast tissue. Invasive lobular carcinoma makes up a small portion of all breast cancers.
Invasive ductal carcinoma IDC is the most common type of breast cancer accounting for about 80 percent of these cancers. IDC starts in cells that line the milk ducts. Hence this tumor is also called Ductal Carcinoma In Situ of Breast with Microinvasion.
Ductal carcinoma in situ DCIS is the presence of abnormal cells inside a milk duct in the breast. The most common type of breast cancer begins in the breast ducts invasive ductal carcinoma. They usually occur in a background of in situ carcinomas such as high-grade ductal carcinoma in situ and the invasive component by definition is less than 1 mm.
Kinds of Breast Cancer. IDC Invasive Ductal Carcinoma. NST stands for No Special Type.
Regional invasive breast cancer recurrence. DCIS is considered the earliest form of breast cancer. Cancer starts when cells begin to grow out of control.
Less Common Subtypes of Invasive Ductal Carcinoma can include tubular medullary mucinous papillary and cribriform carcinomas of the breast. Invasive ductal carcinoma IDC which is sometimes called infiltrating ductal carcinoma is a cancer in the milk ducts of the breast that has invaded nearby breast tissue. Invasive cancer means the cancer cells have broken out of the lobule where they began and have the potential to spread to the lymph nodes and other areas of the body.
What is invasive breast cancer NST. It is the most common type of breast cancer and approximately 80 of invasive breast cancers are invasive ductal carcinomas. It hasnt spread beyond the duct where it started.
Invasive breast cancer means that the cancer cells have grown through the lining of the ducts into the surrounding breast tissue. Invasive Breast Cancer IDCILC Breast cancers that have spread into surrounding breast tissue are known as invasive breast cancer. Stage 2 breast cancer is considered invasive meaning that cancer cells have broken out of the ducts or lobules of the breast.
Definition of Non-Invasive Breast Cancer A non-invasive carcinoma also known as an in-situ carcinoma is a term used to describe the malignant transformation of epithelial cells that remain in their original site without invading the basement membrane. This is not the same as metastatic stage 4 breast cancer. These invasive cancer cells can also spread to other parts of the body.
Invasive cancer cells can also spread or metastasize to other parts of the body. To learn more about how cancers start and spread see What Is Cancer Breast cancer cells usually form a tumor that can often be seen on an x-ray or felt as a lump. DCIS is a noninvasive breast cancer of the milk duct.
Microinvasive Carcinomas of Breast are rare tumors of the breast. Invasive breast cancer involving the same breast parenchyma as the original primary. Invasive ductal carcinoma also called infiltrating ductal carcinoma is the most common type of breast cancer accounting for about 80 of all cases of breast cancer.
If abnormal cells move beyond the layer of tissue where they originated the cells become. Invasive carcinoma of no special type NST also known as invasive ductal carcinoma or ductal NOS and previously known as invasive ductal carcinoma not otherwise specified NOS is a group of breast cancers that do not have the specific differentiating features. The two most common are invasive ductal carcinoma and invasive lobular carcinoma.
Women in the US.