A score between 10 to 25 means you have low bone density osteopenia. Some authors advocate a definition of a high BMD where the Z-score is 25 to highlight to clinicians the potential for underlying pathology 2.
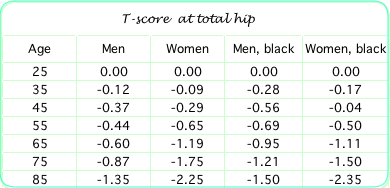
These numbers do not express z scores but are actual bone density.
Bone density z score. A lower Z-score means your BMD is lower and a higher Z-score means its higher. Your bone density test result also includes a Z-score that compares your bone density to what is normal in someone your age and body size. Lumbar Spine total bone mineral density 0767 gmcm2 T score -25 and Z score -14 Osteoporosis fracture risk High.
Scores indicate the amount ones bone mineral density varies from the mean. Your bone density test results are reported in two numbers. Z-score is the measure of the density of a persons bone in comparison to whats expected in a person of equivalent age sex and size.
Women with lower BMD but not yet osteoporosis may wish to pursue. For instance if your Z score is 20 or more it means that very few people your age have a bone density that low and it signals the need for a complete medical workup looking for all possible cause of excessive bone loss. Most experts recommend using Z-scores rather than T-scores for children teens women still having periods and younger men.
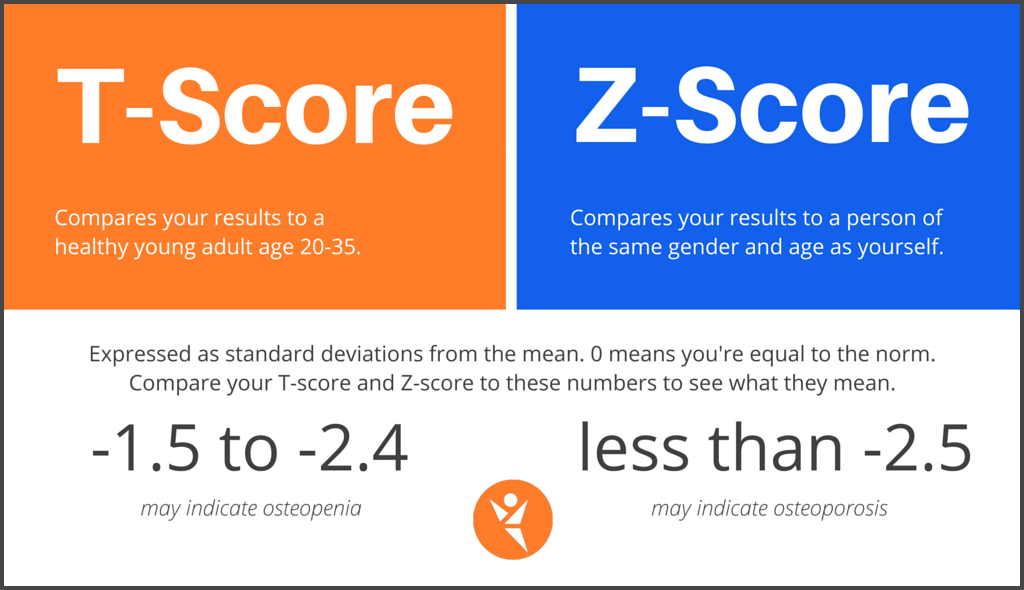
The young normal or T-score indicates how your BMD compares to that of a healthy 30 year-old. A Z score on the other hand assesses your bone density in comparison to the bone density found in other individuals of your same demographic. Less than 05 of patients who underwent DXA-scanning were found to have a T- or Z-score of more than 40 often the cause of an unusually high bone mass HBM and associated with mild skeletal dysplasia and the inability to float in water.
Pediatricians use percentiles to interpret the height of a child. A normal BMD Z-score ranges from -25 to 25 3 4. The Z-score is the number of standard deviations away from the average value of the reference group.
For example if you are a 60-year-old female a Z-score compares your bone density to the average bone density of 60-year-old females. If the Z-score is -084 then 20 of people have a lower bone density. Peak bone density is reached by age 30 and should ideally be maintained at this level throughout your life.
Any post menopausal woman should always request her T-score rather than just her Z-score. The osteoporosis Z-score on the other hand represents a womans bone density results in comparison to a person of her age sex weight and ethnicity. A low Z-score below -20 is a warning sign that you have less bone mass andor may be losing bone more rapidly than expected for someone your age.
Treatment depends upon the stage of osteoporosis. Among older adults low bone mineral density is common so Z-scores can be misleading. The T-score is in units of standard.
Your T-score is your bone density compared with what is normally expected in a healthy young adult of your sex. A person who is average has a Z-score of zero and is at the 50th percentile. If your Z-score is -2 or below your bone density is worse than average for people of your demographic characteristics.
Normal Range of Z-Score. A Z score below -20 means that you have less bone mass than someone. If ones Z-score is abnormally skewed this could represent an external factor aside from aging that is causing atypical bone loss.
Your doctor will interpret your T-score in relation to your physical exam risks and medical history and explain what your bone density scan results mean to you. The percentile is the percent of people in the population who have a lower bone density. Left hip total bone mineral density is 0794 gmcm2 T score -12 and Z score -05 Osteopenia fracture risk increased.
Epidemiology of bone loss. A Z-score compares your bone density to the average bone density of people your own age and gender. Hunter D and Sambrook PN.
A high bone mineral density is one where the bone mineral density BMD is usually greater than two standard deviations above what is expected for age. As BMD decreases from this peak density fracture risk increases. A score of 25 or below means you have osteoporosis.
What Do I Do If I Have A Low Bone Mineral Density Score. In general a negative number on your bone density scan results indicates some bone loss and a higher negative number suggests that your chances of acquiring a bone fracture are greater than normal. Why would a bone density of 0675gmcm2 give a t score of -22 at left hip but a bone density of 0681grcm2 which is higher than 0675grcm2 at lumbar spine give a t-score of -33.
It must be noted that the T-score can predict fracture risk better than the Z-score. This can sometimes be seen on routine DXA scan assessment. A low Z-score is associated with secondary osteoporosis.
Your T-score is the number of units called standard deviations that your bone density is above or below the average. Negative scores indicate lower bone density and positive scores indicate higher. If your Z-score is -1 0 or a positive number your bone density is comparable to that of other people of your demographic characteristics.
A Z-score compares your bone density to the average values for a person of your same age and gender. The Z-score report meanwhile shows deviations of above or below the bone density level from an expected bone density according to a normal persons age sex race and weight. This report is useful for it helps determine the type of osteoporosis and the causes for the abnormal bone loss.
The Z score is an indication of how much bone mass you have compared with other people of your age gender and size. A normal Z-score means that you have a similar BMD to other healthy people in your age group.
They experiment with bags of cereal to make the connection between bone density and bone strength. The proximal femoral bone loses 15 percent of its mass per month or roughly 10 percent over a six-month stay in space with the recovery after returning to Earth taking at least three or four years.
 What Happens To Bones In Space Canadian Space Agency
What Happens To Bones In Space Canadian Space Agency
124 bone loss relative to baseline per month when on Mars.
Bone density loss in space. This drop in density known as disuse osteoporosis leaves bone weak and less able to support the bodys weight and movement upon return to Earth putting the astronaut at a higher risk of fracture. Diminishing bone mass also triggers a rise in calcium levels in the blood which increases the risk of kidney stones. That results in an imbalance between the formation of new bone cells and the removal of old.
For a short-duration flight bone loss is a fairly minor consequence. In microgravity bones do not bear the loads of body weight so the production of osteoblasts decreases. Without gravity to create the resistance needed for weight-bearing exercise bones do not get the healthy stress they need to build and remodel.
On a long-duration space flight such as those planned for missions to Mars and beyond bone loss can be a serious impediment. Spaceflight osteopenia refers to the characteristic bone loss that occurs during spaceflight. The high amount of calcium found in astronauts blood during spaceflight much higher than on Earth reflects the decrease in bone density or bone mass.
Six months to Mars 18 months there six months back. Spacefarers typically experience bone loss in the lower halves of their bodies particularly in the lumbar vertebrae and the leg bones. The measurement of bone mineral density BMD by dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry DXA is the Medical Assessment Test used at the NASA Johnson Space Center to evaluate whether prolonged exposure to spaceflight increases the risk for premature osteoporosis in International Space Station ISS astronauts.
Astronauts on long-term space missions have experienced bone density reduction to the point that it is a major medical concern. So the balance between the cells that break down. Researchers suspect the root cause of bone loss in space is weightlessness.
Students learn about factors that affect bone density including the microgravity environment experienced by Space Station astronauts. NASA has long known that astronauts in space gradually lose muscle strength and bone density over time while. During spaceflight the bone mineral density BMD of crewmembers undergoes substantial changes with some areas of the skeleton such as the bones of the head showing an increase in BMD and some.
Unfortunately without the pull of gravity it is very difficult if not impossible to duplicate loads routinely experienced by our muscles and bones on Earth. Bone loss may be prevented by eating a high-calcium high-vitamin D diet exercising not smoking limiting alcohol consumption and taking medications to prevent osteoporosis. Starting bone density of 091 gcm2 From our first chart and calculations ie.
Factors that may affect bone loss include diet age menopause smoking not exercising and medications such as corticosteroids. The proximal femoral bone loses 15 percent of its mass per month or roughly 10 percent over a six-month stay in space with the recovery after returning to Earth taking at least three or four years. To quantify microgravity-induced bone loss in humans we performed a meta-analysis of studies systematically.
The NASA-funded research is detailed in the online version of the science journal Bone. Although our new exercise regimes are significantly reducing or eliminating the loss of bone mass density studying the structural recovery is still a key part of the puzzle for reducing the risks of broken bones while astronauts operate on the surface of Mars someday. In the microgravity environment of space astronauts lose on average 1 to 2 of their bone mineral density every month.
Published by NASA in 2012. According to this thinking the remedy for bone loss in space should be exercises that duplicate stresses on our muscles and skeletons experienced during a daily and active life on Earth. Bone loss occurs when bone resorption exceeds bone formation.
Astronauts lose an average of more than 1 bone mass per month spent in space. When you go into space and lets say you dont do any kind of physical exercise that stimulus is gone because of the near absence of gravity. Bone loss in space travelers is a major challenge for long-duration space exploration.
1 There is concern that during long-duration flights excessive bone loss and the associated increase in serum calcium ion levels will interfere with execution of mission tasks and result in irreversible skeletal damage. 2 bone loss relative to baseline per month when in transit to and from Mars.
Typical logging sondes use a Cesium-137 source which emits gamma rays of 066MeV. Use a scale to measure the objects weight.
 Which Device Is Used To Measure Density Of Liquid Quora
Which Device Is Used To Measure Density Of Liquid Quora
A hydrometer is a special device used to determine the density of liquids.

What tool measures density. The Portable Density Meter manufactured by Petrosystems is specifically designed with a broad measuring range and has an accurate density measurements in seconds. The drawbacks of Cumulus are that it does not account for dissimilar breast proportions in the images. Let us understand the tools that are used to measure the keyword density of your blog post or article so that you can keep track of the keyword density 1 GeoRanker Keyword Density Checker Tool.
Density is defined as mass per unit volume so it is necessary to measure both the weight and volume of an object to determine its density. Benchtop Portable digital density measuring instruments Agaram Industries is the exclusive distributor of Rudolph Research Analytical from USA who manufacture a wide range of bench-top density meters. This is one of three well logging tools that are commonly used to calculate porosity the other two being sonic logging and neutron porosity logging.
Density logging is a well logging tool that can provide a continuous record of a formations bulk density along the length of a borehole. Coriolis mass flow meter measures density of the flowing fluid from frequency of oscillation of sensor which is mounted on the Coriolis flow tubes. The density more precisely the volumetric mass density.
RRA offers 4 models in their DDM-series density meters. A ruler can be used to measure the dimensions of an object and calculate its volume. Also known as specific mass of a substance is its mass per unit volumeThe symbol most often used for density is r the lower case Greek letter rho although the Latin letter D can also be used.
Some commonly used density measuring devices include hydrometers aerometers pycnometers density kits and digital density meters. The GeoPyc 1360 Envelope Density Analyzer is a revolutionary instrument for rapidly measuring the envelope density of porous objects of irregular size and shape. Bulk density tester is tools to measure bulk density LABULK 0335 Tap Density Tester2 Stations with Printer LABULK 0335 Intelligent Tap Density Tester is an upgrade of AS-100 Tap Density Tester it becomes another success going with the modern technology.
Mathematically density is defined as mass divided by volume. With an installed base of over 175000 densitometers and viscometers worldwide we are at the forefront of concentration and density measurement. The GeoPyc 1360 Envelope Density Analyzer is a revolutionary instrument for rapidly measuring the envelope density of porous objects of irregular size and shape.
The volume of irregularly shaped solids can be found by using the displacement. Measurement with Digital Density Meters. This free density calculator determines any of the three variables in the density equation given the other two.
Density logging tools A density-logging tool sends gamma rays into a formation and detects those that are scattered back. Our density viscosity measurement devices offer unbeatable performance for applications in alcohol concentration API gravity specific gravity and more. Particle Size should exceed 2 mm for best results.
Particle Size should exceed 2 mm for best results. Several commercial tools measure density automated on digital raw mammograms. At this high energy level Compton scattering dominates.
Alcohol BRIX API degrees with high precision and short measuring time. It is labour intense and heavily dependent on the reader skill. Where r is the density m is the mass and V is the volume.
In geology bulk density is a function of the density of the minerals forming a rock and the fluid enclosed in the pore spaces. A similar two-step design was used to train density measures in analogue images. Tools to measure keyword density assist marketers in balancing their keywords in more appropriate proportion.
Density Determination of Liquids with Digital Density Meters If more than just the density is of interest digital density meters measure density specific gravity and other related attributes of liquid samples ie. Measurements from raw images using FDA approved software iCAD were used as templates for STRATUS to measure density on processed images through machine learning. Relative risks of breast cancer were estimated in three unique datasets.
In addition explore hundreds of other calculators including topics such as finance math health fitness weather and even transportation. Rather than measuring the volume in a graduated cylinder and then needing to weigh the liquid to determine its mass and of course subtracting the weight of its container a hydrometer will float at a different level within a liquid based on its density. Cumulus is the gold standard to measure mammographic density on analogue mammograms.
This value is stable and constant at any particular temperature when the water is devoid of any impurities. At room temperature 20 C the density value is 1 gcm 3 or 1000 kgm 3.
 The Oceans 3 2 The Density Of Fresh Water And Seawater Openlearn Open University S206 1
The Oceans 3 2 The Density Of Fresh Water And Seawater Openlearn Open University S206 1
Freezing water expands over 9 by volume and ice floats on water because it is lighter.

What is the density of water. Solid liquid and gas. What is the Density of Water. When water freezes it expands rapidly adding about 9 by volume.
The usual value used in calculations is 1 gram per milliliter 1 gml or 1 gram per cubic centimeter 1 gcm 3. Although the density of water is pretty close to 1 gmL certain disciplines of science need to know the density of water with a higher specificity. Sensible Heat it is the quantity of heat contained in 1 kg of water according to the selected temperature.
The density of water varies with temperature and impurities. The density of a substance is the same regardless of the size of the sample. For most purposes its enough to know that the density of water is 1000 kgm 3However as with almost all materials its density changes with temperature.
Water density changes with temperature and salinity. The density of water is 1 gram per cubic centimeter. Liquid water has a density of about 1 kgdm 3 making any of these SI units numerically convenient to use as most solids and liquids have densities between 01 and 20 kgdm 3.
Density is commonly expressed in units of grams per cubic centimetre. Its no coincidence that water has a density of 1. Water is the only substance on Earth that exists in all three physical states of matter.
Density of Water H 2 O Pure water has its highest density 1000 kgm3 at temperature 398oC 392oF. It has a maximum of density at 398 C 1000 kgm 3 whereas the density of ice is 917 kgm 3. Density is mass divided by volume rmv and water was used as the basis for establishing the metric unit of mass which means a cubic centimeter 1cm 3 of water weighs one gram 1g.
Density is an intensive property at any particular temperature. As the temperature increases the density rises to a peak at 398 C 3916 F and then decreases. Water is densest at 398C and is least dense at 0C freezing point.
For example the density of water is 1 gram per cubic centimetre and Earth s density is 551 grams per cubic centimetre. Density can also be expressed as kilograms per cubic metre in metre-kilogram-second or SI units. The density of water is about 1 gram per cubic centimetre 62 lbcu ft.
Fresh water has a maximum density at around 4 Celsius. Kilogram per cubic decimetre kgdm 3. The density of water is the weight of the water per its unit volume which depends on the temperature of the water.
While you can round the density to 1 gram per milliliter there are more precise values for you to use. The density of pure water is altered by temperature. The density of water is approximately 1000 kgm3 and the density of air is approximately 12 kgm3.
The density of water varies according to temperature and the degree of purity. Ratio of the mass of water kg occupied in a volume of 1 m3. The density of water is 1940 slft 3 at 39 F 4 C and the specific weight in Imperial units is g 1940 slft3 32174 fts2 1940 lb f fts2 ft3 32174 fts2 624 lb f ft3 See more about the difference between mass and weight Online Water density Calculator.
It is temperature-dependent but this relation is said to be non- linear and also it is unimodal in nature rather than monotonic. This relationship was originally used to define the gram. The density varies with temperature but not linearly.
The density of water is most given as 1 gcm3 but below is the density of water with different units. Density of pure water is a constant at a certain temperature not depending on sample. With respect to the definition the density formula is represented as Density r Mass mVolume V.
Density is measured as mass g per unit of volume cm³. In other words at the same temperature the density of water in gml or gcm 3 is 099777. If solid objects are placed in water and they sink they have a density greater than water 1000.
However we have a slight but a super important anomaly when it comes to water. At room temperature ie 22 C the density of water in kgm 3 is 99777. The density of water is around approximately 1 gram cubic centimetre 1 gcm3.
At 4 degrees Celsius pure water has a density of 1gmL or 1kgL and a specific gravity of 1. Water density increases as the temperature gets colder. Water differs from most liquids in that it becomes less dense as it freezes.