The deep zone which contains about 80 percent of the oceans volume has relatively stable temperature and salinity patterns. Some ocean salts come from underwater volcanic eruptions which directly release minerals into the ocean.
It is measured in unit of PSU Practical Salinity Unit which is a unit based on the properties of sea water conductivity.
Salinity of the ocean. It is generally expressed as parts per thousand ppt. The oceans are types of basins on the surface of the earth which containing saltwater. The average salinity of the ocean 352 or 35 parts of salt in 1000 parts of water.
Salinity means the total content of dissolved salts in Sea or Ocean. Magnesium and sulfate make up another 10 percent of the total. This implies that in the total weight of ocean water dissolved salts amount to 35 percent.
The salinity of the ocean varies from place to place especially at the surface. Its long-term trend middle has a remarkably similar pattern. Seawater or salt water is water from a sea or oceanOn average seawater in the worlds oceans has a salinity of about 35 35 gl 35 ppt 599 mM.
Of the total salt content in sea water about 77 per cent is sodium chloride or common salt. Although everyone knows that seawater is salty few know that even small variations in ocean surface salinity ie concentration of dissolved salts can have dramatic effects on the water cycle and ocean circulation. There is a pronounced difference in temperature and salinity between the surface and deep zones of the Pacific.
Salinity of Ocean Water. The average salinity of seawater is about 35 parts per thousand or 35 percent of total mass. Together they make up around 85 percent of all dissolved ions in the ocean.
When an ocean is located nearby the equator the salinity is lower. Salinity is calculated as the amount of salt dissolved in 1000 gm of seawater. The equatorial region of the Atlantic Ocean has a salinity of about 35.
It is seen from the chemical analysis that the sea water on the average contains 3½ per cent of salt it means every 1000 grams of sea water contains nearly 35 grams of salt. Sodium chloride or the common salt is the most common among all the dissolved salts in the sea. Places of higher salinity There are parts of the ocean where hardly any rain falls but warm dry winds cause lots of evaporation.
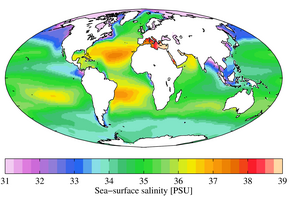
The geographic distribution of surface salinity varies. Much of the ocean has salinity between 34 ppt and 36 ppt but there are places that tend to be higher or lower. The dept of the ocean plays a part too.
In the deeper part of the ocean it slowly decreases. A salinity of 247 has been regarded as the upper limit to fix brackish water. The salinity of ocean water is usually around 35 parts per thousand on an average at zero degrees Celsius.
Its average temperature is 383 F 35 C. It is equivalent to per thousand or o00 or to gkg. The salinity increases again starting from 1000 metres deep into the water.
Ocean salinity is generally defined as the salt concentration eg Sodium and Chlorure in sea water. We know that sea water is salty. 0-2000 mean salinity climatology top shows the relatively fresh Pacific versus the salty Atlantic northern Indian Ocean.
The highest salinity is not observed at the equator rather it is recorded between 15 0-20 0 latitudes. Ocean salinity at different latitudes in the Atlantic and Pacific. The average salinity of the Atlantic Ocean is 3567 0 00.
Rivers and lakes can have a wide range of salinities from less than 001 gkg 3 to a few gkg although there are many places where higher salinities are found. The salinity of the Great Salt Lake Utah USA the Dead Sea and the Lake Van in Turkey are 220 240 and 330 respectively. The upper part of the ocean has the most salinity because thats where evaporation mainly happens.
This means that every kilogram roughly one liter by volume of seawater has approximately 35 grams 12 oz of dissolved salts predominantly sodium Na. Near the equator there is heavy rainfall high relative humidity cloudiness and calm air of the doldrums. The salinity of ocean water is a measure of the concentration of dissolved salts which are mostly sodium chloride but also include salts containing magnesium sulfur calcium and potassium.
Throughout Earths history certain processes have served to make the ocean salty. Salinity is defined as the total amount of dissolved material in grams in one kilogram of seawater. The average salinity of the Atlantic Ocean is around 36-37.
The Dead Sea located between Israel and Jordan is the saltiest body of water in the world with a salinity level or 330000 ppm or 330 ppt making it nearly 10 times saltier than the worlds oceans. Two of the most prevalent ions in seawater are chloride and sodium. Seawater typically has a mass salinity of around 35 gkg although lower values are typical near coasts where rivers enter the ocean.