Because undifferentiated connective tissue UCTD disease can affect so many different parts of the body as an autoimmune disease UCTD often has many symptoms. Diagnosis requires a thorough review of systems and a physical examination.
 Systemic Connective Tissue Diseases
Systemic Connective Tissue Diseases
Theres no cure for mixed connective tissue disease.
Connective tissue disease symptoms rash. Note that four of the nine American College of Rheumatology criteria for SLE are skin signs ie malar butterfly rash discoid plaques photosensitivity and oral ulcers. It sometimes occurs months or years before other symptoms. Additional symptoms of MCTD vary from person to person but some of the most common include.
Joint stiffness shortness of breath difficulty swallowing rash or other skin changes or. But they are other symptoms of other connective tissue diseases that get mixed with others. Rashes and autoimmune connective tissue disease.
Muscle weakness may progress over weeks to months. Common symptoms of undifferentiated connective tissue disease include. These may occur suddenly or develop over months.
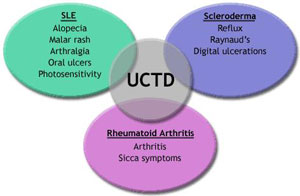
Systemic lupus erythematosus SLE typically affects many organ systems. It does have clinical features of lupus-like rashes on the body skin lesions joint pain headaches etc. Diagnostic criteria for SLE related to the skin and mucous membranes include malar rash discoid rash photosensitivity and oral ulcers.
Other symptoms and signs can include. List of causes of Connective tissue itch and Connective tissue rash alternative diagnoses rare causes misdiagnoses patient stories and much more. Mixed connective tissue disease has features of 3 other connective tissue diseases.
Undifferentiated connective tissue disease UCTD is a condition in which a patients symptoms dont quite meet the criteria the markers or indicators doctors use to make a diagnosis of a well-defined connective tissue disease such as rheumatoid arthritis RA lupus or scleroderma. Polyarthralgias Raynaud syndrome dysphagia pulmonary symptoms eg cough dyspnea and constitutional complaints notably fever fatigue and weight loss may also occur. The symptoms of undifferentiated connective tissue disease may vary from person to person and may change over time.
Signs and symptoms of mixed connective tissue disease can include. An inflammatory disease that can affect many different organs. Raynaud phenomenon a condition in which the blood vessels do not bring enough blood to the hands and feet.
Heliotrope rash is caused by dermatomyositis DM a rare connective tissue disease. Treatment depends on how severe the disease is and the organs involved. Rash muscle pain joint pain swollen fingers swollen hands and.
Symptoms include fever fatigue joint pains weakness and skin rashes on the face neck and upper body. More common signs and symptoms include. Complications may include calcium deposits in muscles or skin.
Pain in multiple joints. In later stages some organs such as the lungs heart and kidneys can be affected. Its symptoms are generally a skin rash and worsening muscle weakness over time.
Dermatomyositis DM is a long-term inflammatory disorder which affects skin and the muscles. Was this article helpful. Severe disease is characterized by dysphagia dysphonia andor diaphragmatic weakness.
The symptoms of mixed connective tissue disease include fatigue joint pain pulmonary hypertension swollen fingers and Raynauds syndrome. Swollen fingers or hands. Connective tissue disease refers to a group of disorders involving the protein-rich tissue that supports organs and other parts of the body.
Autoimmune reactions in which the bodys immune system mistakenly attacks and damages its own tissues cause many connective tissue diseases. Examples of connective tissue are fat bone and. Autoimmune diseases come in a variety of forms each affecting different organs and bodily systems and producing a unique array of symptomsWhile some of these symptoms may often be invisible skin manifestations can often be one of the most visible and telltale signs of autoimmune disease.
Other symptoms may include weight loss fever lung inflammation or light sensitivity. Autoimmune diseases are conditions where the immune system. Skin manifestations of lupus erythematosus are commonly divided into lupus erythematosusspecific and nonspecific disease.
Other associated symptoms and signs can include low-grade fever and Raynauds phenomenon sensitivity numbness and loss of color in the fingers toes ears or nose due to reduced blood flow. Systemic lupus erythematosus SLE. Cause of connective tissue disease.
People with this disease have a violet or bluish-purple rash that develops on areas of the skin. Article updated March 10 2020. Fingers might get puffy and the fingertips become white and numb often in response to cold exposure.
Other connective tissue disease symptoms and signs.
Coronary artery disease is caused by plaque buildup in the wall of the arteries that supply blood to the heart called coronary arteries. The narrowing in your arteries decreases the amount of blood that can flow to your heart.
 Stable Coronary Artery Disease Treatment American Family Physician
Stable Coronary Artery Disease Treatment American Family Physician
What is coronary artery disease.
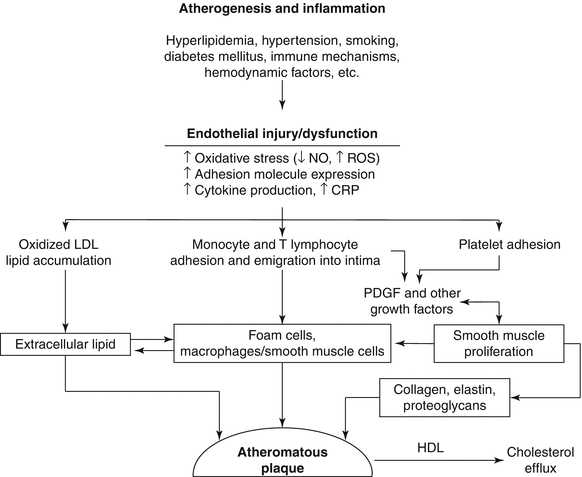
Pathophysiology of coronary artery disease. This condition is usually caused by atherosclerosis. Coronary artery disease is the narrowing or blockage of the coronary arteries. Coronary artery disease CAD is narrowing of the arteries to your heart caused by a buildup of plaque.
Coronary heart disease CHD is usually caused by a build-up of fatty deposits atheroma on the walls of the arteries around the heart coronary arteries. Coronary artery disease is usually caused by a build up cholesterol rich deposits or plaques on the lining inside the artery. The coronary arteries supply blood oxygen and nutrients to your heart.
We review here how these advances have altered our concepts of and clinical approaches to both the chronic and acute phases of CAD. Coronary heart disease also called coronary artery disease or ischemic heart disease disease characterized by an inadequate supply of oxygen-rich blood to the heart muscle myocardium because of narrowing or blocking of a coronary artery by fatty plaques see atherosclerosis. Plaque is made up of cholesterol deposits.
Coronary artery disease develops when the major blood vessels that supply your heart become damaged or diseased. Previously considered a cholesterol storage disease we currently view. CAD occurs when your hearts arteries cant carry necessary oxygen and nutrients to.
Coronary artery disease is almost always due to atheromatous narrowing and subsequent occlusion of the vessel. These plaques are also called atheromatous plaques or simply atheromas. Also called coronary heart disease CHD CAD is the most common form of heart disease and.
This process is called atherosclerosis. We review here how these advances have altered our concepts of and clinical approaches to both the chronic and acute phases of CAD. This process is called atherosclerosis.
During the past decade our understanding of the pathophysiology of coronary artery disease CAD has undergone a remarkable evolution. Coronary heart disease CHD is usually caused by a build-up of fatty deposits on or inside the walls of the coronary arteries. Coronary artery disease CAD also called coronary heart disease CHD ischemic heart disease IHD or simply heart disease involves the reduction of blood flow to the heart muscle due to build-up of plaque atherosclerosis in the arteries of the heart.
The build-up of atheroma makes the arteries narrower restricting the flow of blood to the heart muscle. This causes your heart to get less oxygen. Cholesterol-containing deposits plaques in your coronary arteries and inflammation are usually to blame for coronary artery disease.
Clinical presentations include silent ischemia angina pectoris acute coronary syndromes unstable angina myocardial infarction and sudden cardiac death. Atherosclerosis is the build-up of cholesterol and fatty deposits called plaques inside the arteries. Coronary artery disease also called CAD coronary or atherosclerotic heart disease is a serious condition caused by a buildup of plaque in your coronary arteries the blood vessels that bring.
These plaques can clog the arteries or damage the arteries which limits or stops blood flow to the heart muscle. During the past decade our understanding of the pathophysiology of coronary artery disease CAD has undergone a remarkable evolution. The fatty deposits called atheroma are made up of cholesterol and other waste substances.
Early atheroma from the Greek athera porridge and oma lump is present from young adulthood onwards. Coronary artery disease CAD involves impairment of blood flow through the coronary arteries most commonly by atheromas. A mature plaque is composed of two constituents each associated with a particular cell population.
Coronary artery disease CAD causes impaired blood flow in the arteries that supply blood to the heart. Plaque is made up of cholesterol and other substances. Starting as early as childhood plaque -- a combination of cholesterol fat and other substances -- starts to stick to the walls lining your blood vessels.
We review here how these advances have altered our concepts of and clinical approaches to both the chronic and acute phases of CAD. It is the most common of the cardiovascular diseases. Coronary artery disease CAD also called coronary heart disease is the most common type of heart disease.
Plaque buildup causes the inside of the arteries to narrow over time. It builds up over time. During the past decade our understanding of the pathophysiology of coronary artery disease CAD has undergone a remarkable evolution.
Types include stable angina unstable angina myocardial infarction and sudden.
For patients who have already had transient or mild stroke symptoms due to moderate carotid stenosis 50 to 69 percent surgery reduces the 5-year risk of stroke or death by 65 percent. During carotid endarterectomy the surgeon reduces the risk of stroke from the operation by shunting using a plastic tube to re-route blood flow to the brain and monitoring the patient carefully.
 Carotid Endarterectomy Cea Part 1 Alan B Lumsden Md Youtube
Carotid Endarterectomy Cea Part 1 Alan B Lumsden Md Youtube
This is known as carotid artery disease or carotid artery stenosis and it significantly increases your risk of having a stroke or transient ischaemic attack TIA.
Carotid artery disease surgery. Carotid endarterectomy is the most common form of surgery for severe carotid artery disease. This can reduce the blood supply to your brain and cause a stroke. The surgery to clear a blocked artery is called a carotid endarterectomy CEA.
Blood flow in this artery can become partly or totally blocked by fatty material called plaque. This will increase blood flow to. Carotid endarterectomy surgery is not without risks especially for those who have chronic health conditions such as diabetes hypertension or other diseases.
Carotid artery disease is a disease in which a waxy substance called plaque builds up inside the carotid arteries. What Medical Procedures Treat Carotid Artery Disease. A surgery called carotid endarterectomy CEA is one way to remove blockages to the normal flow of blood and to minimize your risk of a stroke.
Carotid artery stenting is another surgical treatment that is sometimes used to treat carotid artery disease. A TIA is a temporary shortage of blood flow to your brain. During this procedure a surgeon will open the blood vessel and remove any plaque that has built up.
The UCSF Vascular Surgery Program has also earned the highest designation for quality outcomes in carotid artery surgery by the Leapfrog Initiative that compared outcomes in carotid artery surgeries throughout Northern California. Carotid Endarterectomy CEA Carotid endarterectomy is the most commonly performed surgical treatment for carotid artery disease. Potential risks include a stroke heart attack or even death.
You have one of these arteries on each side of your neck. How long are you in the hospital after carotid artery surgery. The artery is repaired with either stitches or a graft.
During this procedure a surgeon threads a tube or catheter through an artery in the groin or arm and passes it up to the carotid artery. A tiny balloon at the end of the tube is then inflated to enlarge the narrowed portion of the artery. After your anesthesiologist gives you local or general anesthesia your doctor will make an incision on.
After making an incision along the front of your neck the surgeon opens the affected carotid artery and removes the plaques. A carotid endarterectomy may be needed if one or both of your carotid arteries become narrowed because of a build-up of fatty deposits plaque. The carotid arteries are the pulsatile structures on either side of the neck which supply the preponderance of blood flow to the brain.
When a carotid artery has a blockage of 70 percent or more doctors may recommend carotid endarterectomy surgery to remove the plaque and restore normal blood flow to the brain. Carotid artery disease develops slowly. Carotid artery disease refers to the build-up of atherosclerotic plaque in one or both common and internal carotid arteries resulting in stenosis or occlusion.
Carotid endarterectomy is a type of surgery used to reduce the risk of stroke from carotid artery disease. Why carotid artery disease develops. A CEA is also known as carotid artery surgery.
Carotid endarterectomy removes plaque from the carotid artery. They are the carotid arteries and they take blood to the brain. If you have a blocked artery you may wonder if you need a CEA.
Treatment of carotid artery disease usually involves a combination of lifestyle changes medication and sometimes surgery. If there is severe narrowing or blockage in the carotid artery a procedure can be done to open the artery. The carotid artery brings needed blood to your brain and face.
The majority of carotid artery disease is asymptomatic but it is also responsible for approximately 10-15 of ischaemic strokes due to plaque rupture andor atheroembolism. Carotid endarterectomy the most common treatment for severe carotid artery disease. Routine physical exams include the physician using a stethoscope to listen to your heart and certain blood vessels.
It is the third most common kind of cardiovascular surgery in the United States. If one is blocked it can lead to a stroke. Narrowing or blockages of these arteries are a significant cause of most strokes and therefore prevention diagnosis and treatment are very important.
A whistling sound or bruit coming from the carotid artery may indicate plaque is building up inside the artery and lead your doctor to recommend you see a vascular surgeon. Unfortunately this surgery is not without risk. The first sign that you have the condition may be a stroke or transient ischemic attack TIA.
During the operation the surgeon peels the plaque away from the carotid artery. Carotid artery surgery is a procedure to treat carotid artery disease.