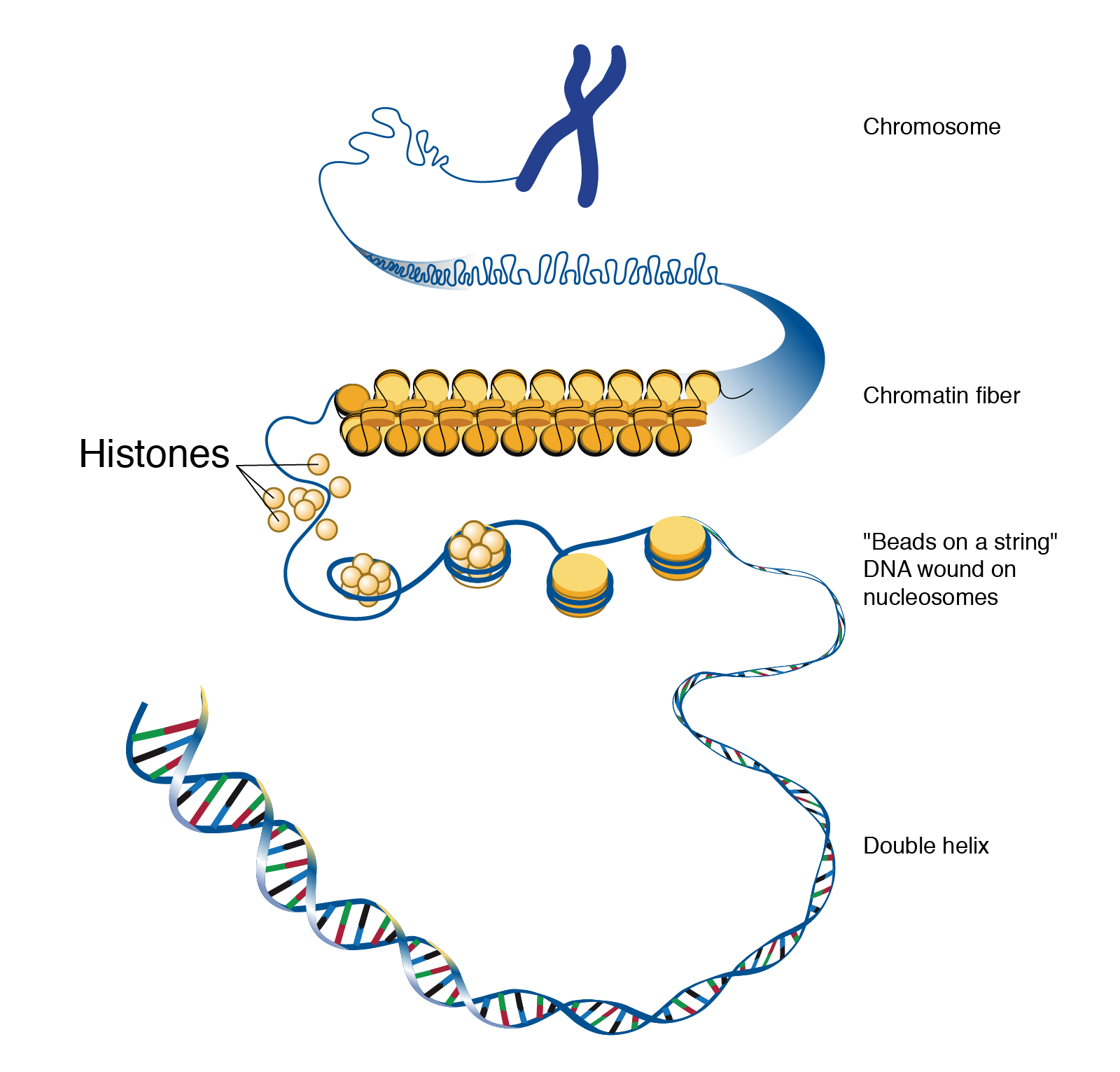
Series of small proteins called histones. Hence histones are a major component of chromatin.
What Is The Role Of Histone In Packaging Dna Quora
Some histones function as spools for the thread-like DNA to wrap around.
What is the function of histone proteins. Histones H2A H2B H3 and H4 are known as the core histones and they come together to form one nucleosome. In biology histones are highly basic proteins found in eukaryotic cell nuclei that pack and order the DNA into structural units called nucleosomes. Indeed non-histone protein acetylation is involved in key cellular processes relevant to physiology and disease such as gene transcription DNA damage repair cell division signal transduction protein folding autophagy and metabolism.
DNA and histones comprise chromatin forming the bulk of eukaryotic chromosome. The Non histone proteins have three important roles in maintaining structure of chromosomes during cell division. Therefore they serve as spools around which DNA winds.
Histones are abundant in lysine and arginine. The proteins other than histone comes under non histone proteinsThe function of non histone proteins vary from one to another. The beads are called nucleosomes.
A histone is a protein that provides structural support to a chromosome. In chromatin those protein which remain after the histone proteins are called non histone proteins. Nonhistone proteins act as the scaffolding structure of chromatin.
The main function of histone proteins is to package and order the DNA into structural units called nucleosomes. Histones are basic proteins and their positive charges allow them to associate with DNA which is negatively charged. In chromatin those proteins which remain after the histones have been removed are classified as non-histone proteins.
The major function of histone proteins is to act as spools for DNA to wind and stabilize. Histones are a family of basic proteins that associate with DNA in the nucleus and help condense it into chromatin. The non-histone proteins are a large group of heterogeneous proteins that play a role in organization and compaction of the chromosome into higher order structuresThey play vital roles in regulating processes like nucleosome remodeling DNA replication RNA synthesis and processing nuclear transport steroid hormone action and interphasemitosis transition.
Histones are proteins that condense and structure the DNA of eukaryotic cell nuclei into units called nucleosomes. The five types of histones are H1 H2A H2B H3 and H4. 16K views View 1 Upvoter.
Histone chaperones form a separate group of proteins differing in structure and mode of interactions with histones compared to ATP-dependent chromatin remodelers and enzymes modifying histones post-translationally. Some variants of histones are associated with the regulation of gene expression. Chromatin refers to the pack of nucleosomes.
They are the chief protein components of. Here we summarize a suite of analysis tools and applications we have employed to characterize H1 variants and mutations. Each nucleosome is made of DNA wrapped around eight histone proteins that function like a spool and are called a histone octamer.
But the function of histone is to compress Dna around it in spiral manner and hence the Dna which is more larger than a cell is concentrated inside the nucleus. Under the microscope in its extended form chromatin looks like beads on a string. Four of them called H2A H2B H3 and H4 contribute two molecules each to form an octamer an eight-part.
In order for very long DNA molecules to fit into the cell nucleus they wrap around complexes of histone proteins giving the chromosome a more compact shape. Their chief functions are to compact and control the long threads of DNA. Histones are the chief protein components of chromatin acting as spools around which DNA winds and playing a role in gene regulation.
There are five classes of histone. Histones are a type of positively-charged proteins that serve as the basic type of proteins found in the chromosomes. The main function of histone proteins is to help in the condensed packaging of DNA inside the nucleus.
The interaction between histones and DNA is shown in figure 1. If histone proteins are removed from chromatin the remaining protein part can be referred as nonhistone proteins. Their main functions are to compact DNA and regulate chromatin therefore impacting gene regulation.
Scaffold proteins DNA polymerase heterochromatin protein 1 and polycomb are the non histone proteins. In biology histones are highly alkaline proteins found in eukaryotic cell nuclei that package and order the DNA into structural units called nucleosomes. Histones are basic proteins of major importance in packaging of eukaryotic DNA.
DNA is normally conceived of as a spiral ladder but in eukaryotic cells cells with nuclei the DNA in the nucleus is strung around a series of spool-shaped proteins known as histones. This is the main difference between histone and nonhistone proteins. Histones are composed of positively charged amino acids that bind tightly to and neutralize the negative charges of DNA.
Linker histone H1 the key chromatin structural protein facilitating higher order chromatin folding is emerging as an important epigenetic mark and regulator for gene expression and cellular differentiation. Each histone octamer is composed of two copies each of the histone proteins H2A H2B H3 and H4.