Bypass metabolism such as alternative oxidoreductases have been discovered in both organisms. Because several resistance mechanisms inhibit the action of more than one different drug class these will be discussed after the properties of the each of antibiotics have been described.
 Genes Free Full Text The Complex Relationship Between Virulence And Antibiotic Resistance Html
Genes Free Full Text The Complex Relationship Between Virulence And Antibiotic Resistance Html
Department of Internal Medicine.

Mechanisms of antibiotic resistance summary. In summary the articles within. Virulence Mechanisms of Bacterial Pathogens. Vaginalis is well documented and the principal mechanisms have been defined.
There are two important types of genetic mechanisms that can give rise to antibiotic resistance. Pneumoniae involves genetic mutations that alter penicillin-binding protein structure and results in decreased affinity for all beta-lactam antibiotics. Each year in the US millions of people suffer from antibiotic-resistant.
Antibiotic resistance occurs naturally but misuse of antibiotics in humans and animals is accelerating the process. Mechanisms of Antibiotic Resistance. The mechanism of amino-lactam resistance of S.
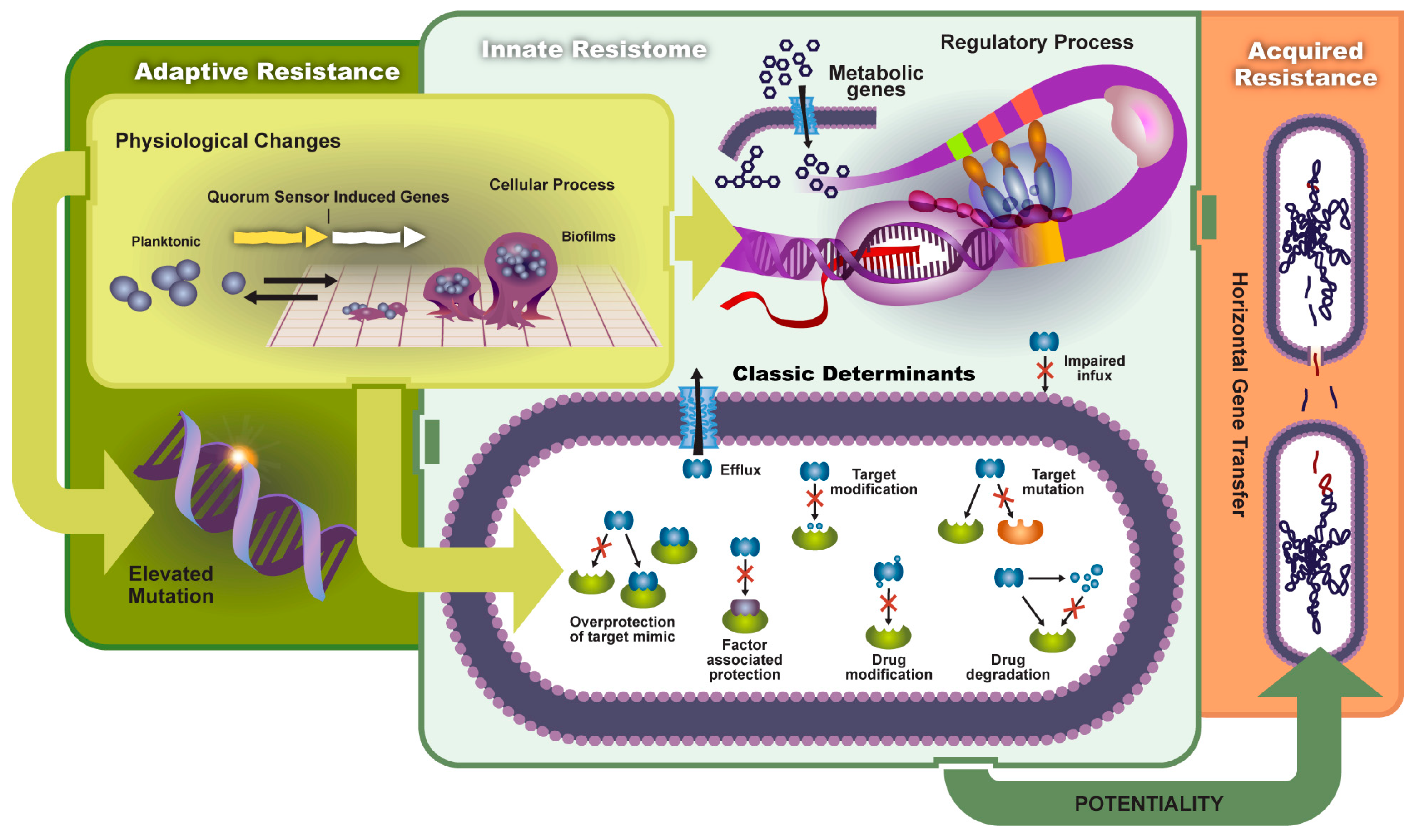
2 Inactivation of the antibody 3 Alteration of the antibiotics target 4 failure to trip the antibody 5. Antimicrobial resistance quickly emerged to reduce the. These mechanisms include enzymatic modification of the drug modification of the antimicrobial target and prevention of drug penetration or accumulation.
The World Health Organization has named antibiotic resistance as one of the three most important public health threats of the 21st century 1. Pathogenic germs become resistant to antibiotics when they develop the ability to defeat the drugs designed to kill them. Changes in penicillin binding proteins.
Antibiotics can have bacteriostatic ie stopping bacterial reproduction bactericidal ie killing bacteria or both mechanisms of action. Mutation and acquisition of new genetic material. There are several common mechanisms for drug resistance which are summarized in Figure PageIndex1.
The advent of antibiotics revolutionized the means by which infectious diseases were treated. 11 This mechanism of resistance is acquired through a process known as natural transformation in which a particular genome encoding the alteration is picked up from other pneumococci and incorporated into their own DNA. Many resistance mechanisms have emerged including alteration of target a DNA-gyrase increased efflux export of a drug out of the microorganism fluoroquinolone inactivation by an aminoglycoside N-acetyltransferase and protection of the target by DNA-binding proteins known as Qnr.
Mutation Target protein Genes Antibiotic Conjugation Resistant gene Plasmid Pilus Transformation Naked DNA Transduction. Your summary should include the terms listed below. Resistance to antibiotics can be caused by four general mechanisms inactivation alteration of the target circumvention of the target pathway or efflux of the antibiotic and bacteria can.
Linezolid It is noteworthy that linezolid is the only completely synthetic antibiotic to act at the ribosome and it is the first new chemical class of antibiotic to be introduced in the 20 years between 1980. Underline each term in your paragraph. Resistance of staphylococci to methicillin and.
However the declaration of victory over bacterial pathogens was premature. A growing number of infections such as pneumonia tuberculosis gonorrhoea and salmonellosis are becoming harder to treat as the antibiotics used to treat them become less effective. Biochemical mechanisms of antibiotic resistance Prevention of drug accumulation in the bacterium Modificationprotection of the target site Use of alternative pathways for metabolic growthrequirements By producing an enzyme that inactivates theantibiotic Quorum sensing.
In the case of mutation the rate at which resistance develops can be attributed to the rate at which bacteria mutate. Mutational changes in original PBPs or acquisition of different PBPs will lead to inability of the antibiotic to bind to the PBP and inhibit cell wall synthesis. Antibiotics are effective against either a small group of bacteria narrow-spectrum or a wide range of pathogens broad-spectrum.
There are different types of antibiotic resistance- 1 restricted entree to aim ie an efflux pump that pumps antibiotics out of cytol. Provides readers with knowledge about the broad field of drug resistance Offers guidance to translate research into tools for prevention diagnosis and treatment of infectious diseases Links strategies to analyze microbes to the development of new drugs socioeconomic impacts to therapeutic strategies and public policies to antibiotic-resistance-prevention strategies. In a well-crafted paragraph summarize the information about all of the mechanisms of antibiotic resistance.
Production of beta-lactamases the enzymes that degrade beta-lactam antibiotics is the most widespread and threatening mechanism of antibiotic resistance. Resistance of Enterobacteriaceae to penicllins cephalosporins and aztreonam. A mutation is a permanent change in an organisms genetic material.
Resistance has been demonstrated for each agent and the mechanism of resistance has been investigated. Metronidazole resistance in T. Mechanisms for Drug Resistance.
Suddenly common infections became easily curable and outbreaks of infectious disease were readily controlled.